Deconstructing BCBS 239: 14 principles for risk excellence
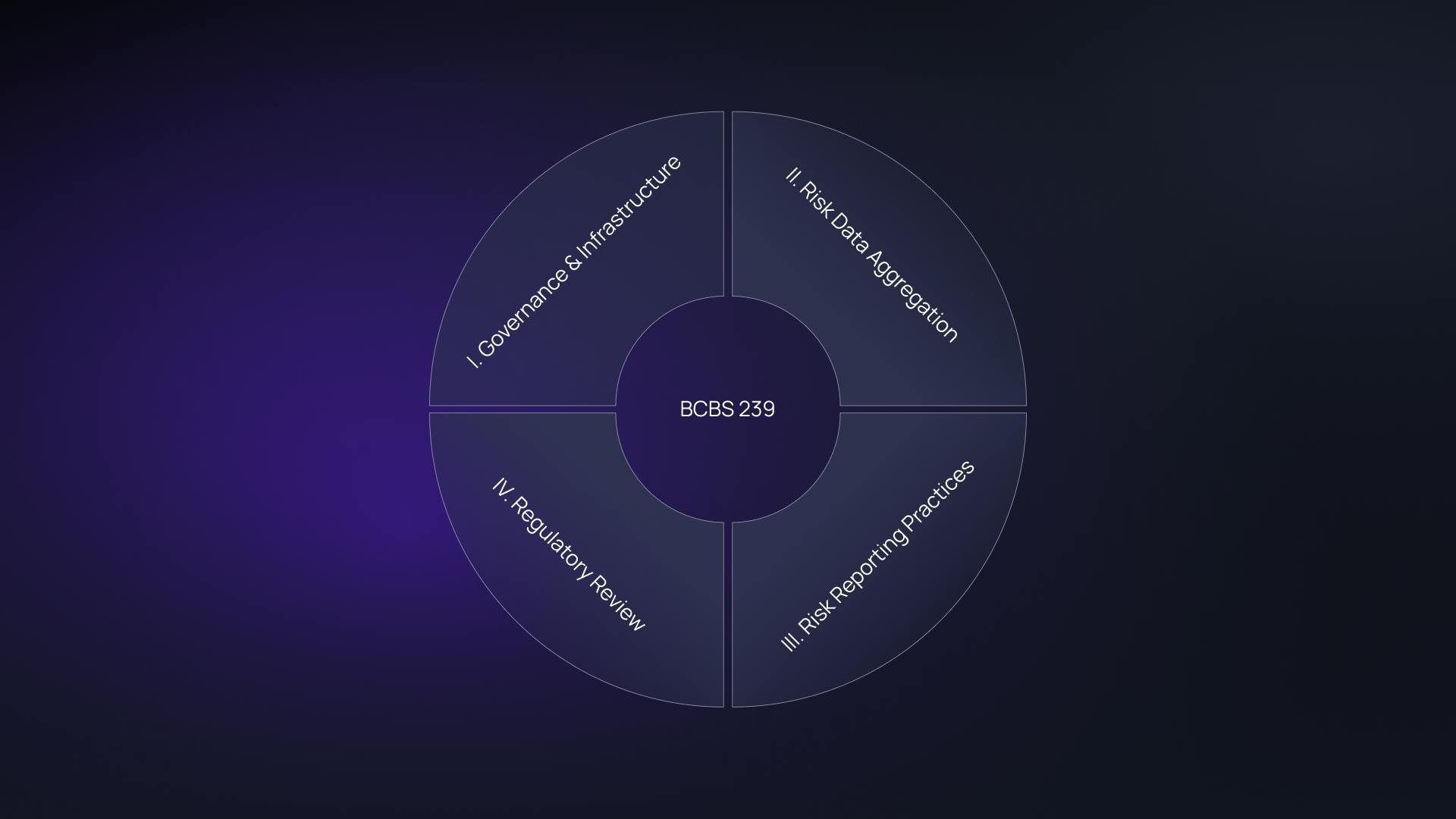
BCBS 239 is organized into four key sections, encompassing 14 principles that set the standard for robust risk management.
I. Overarching governance and infrastructure (Principles 1-2)
This is the foundation. The regulation places ultimate responsibility on a bank's board and senior management to establish a strong data culture and invest in the necessary infrastructure.
Many banks operate with fragmented, legacy systems and siloed data ownership. This makes it nearly impossible for leadership to get a unified view of risk or to enforce consistent data standards across the organization.
II. Risk data aggregation capabilities (Principles 3-6)
This is the technical core of the regulation, where data quality is explicitly put to the test. The principles demand that banks can generate accurate and reliable risk data, both in normal times and during periods of financial stress. Key requirements include:
- Accuracy and Integrity: Risk data must be materially accurate and reconciled with its sources.
- Completeness: A bank must capture all material risk data across the entire institution.
- Timeliness: Risk data must be available in a timely manner to support decision-making.
Traditional, manual data checks are slow, error-prone, and cannot scale to handle the volume and velocity of modern data. Issues like missing data, stale information, and subtle inaccuracies in complex datasets can easily go unnoticed until it's too late
III. Risk reporting practices (Principles 7-11)
High-quality data is useless if it can't be translated into clear, actionable reports. This section ensures that the output of a bank's risk data aggregation is fit for purpose. Reports must be accurate, comprehensive, clear, and distributed to the right parties at the right frequency.
Breaks in the data journey from source to report are common. Reports often lack the necessary granularity, are too complex to be easily understood, or are based on outdated information, rendering them ineffective for proactive decision-making.
IV. Supervisory review, tools, and cooperation (Principles 12-14)
Finally, the regulation empowers supervisors to hold banks accountable, requiring them to conduct regular reviews and remediation when deficiencies are found. This can lead to costly capital add-ons for banks with poor data quality scores.